🔒 Master Python Tuples with M.A.G.I.C.S.
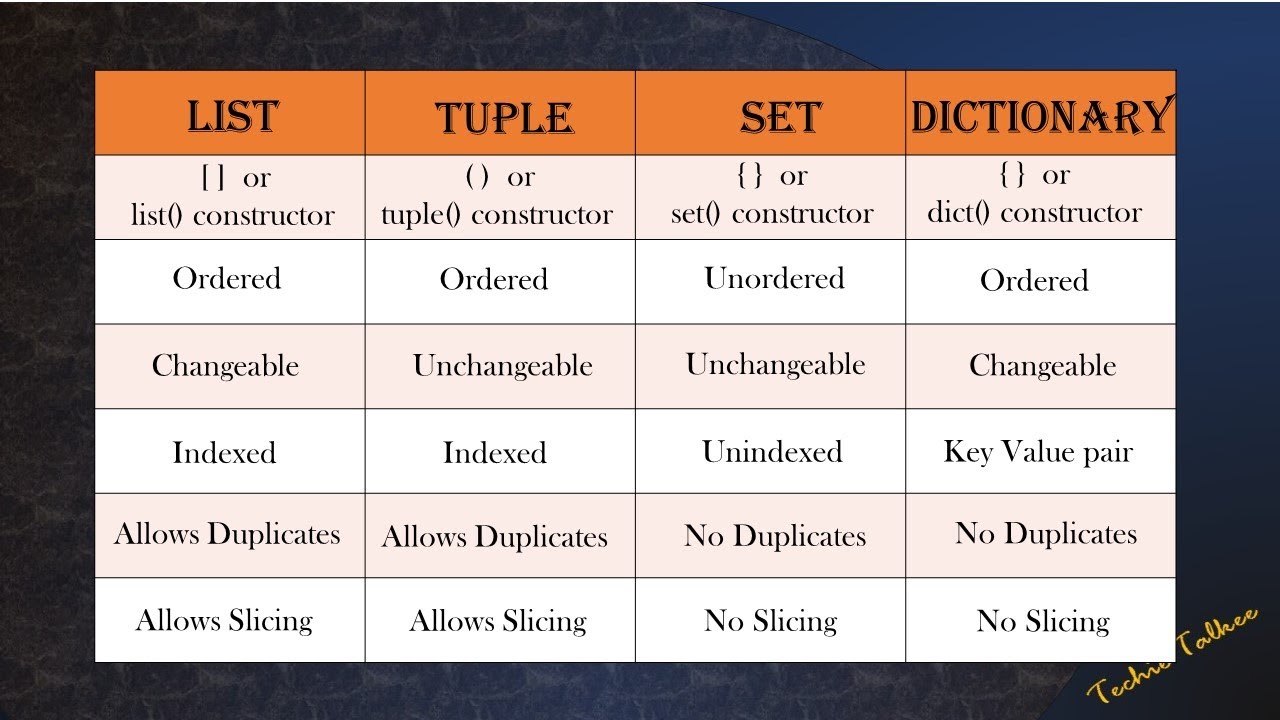
Tuples are lists that cannot be changed. They are faster, lighter, and safer than lists. In Python, we call them “Immutable.”
Because they are locked, the M.A.G.I.C.S. framework looks a little different.
The Framework
| Letter | Category | Status | Key Operations |
| M | Make | ✅ Active | (), tuple(), (x,) |
| A | Add | ❌ Blocked | (Immutable. Cannot add items) |
| G | Get | ✅ Active | t[i], .index(), .count() |
| I | Improve | ⚠️ Limited | Cannot update. Use sorted() |
| C | Clean | ❌ Blocked | (Immutable. Cannot delete items) |
| S | Stats | ✅ Active | min(), max(), sum() |
🟢 1. M – MAKE (Creation)
The tricky part about tuples is creating a tuple with just one item.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Empty Tuple | () | t = () | () |
| Manual | (v1, v2) | t = (1, 2) | (1, 2) |
| No Brackets | v1, v2 | t = 1, 2 | (1, 2) (Pro Move!) |
| Singleton | (x,) | t = (1,) | (1,) (Comma is key!) |
| Convert | tuple(iter) | t = tuple([1, 2]) | (1, 2) |
| Trap! | (x) | t = (1) | 1 (This is just an Integer!) |
🔵 2. A – ADD (Growth)
Tuples are locked. You cannot change them in place. You can only create new ones by combining old ones.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Concatenate | t1 + t2 | t = (1, 2) + (3,) | (1, 2, 3) (New Tuple) |
| Repeat | t * n | t = (0,) * 3 | (0, 0, 0) |
| Append? | ❌ | t.append(1) | AttributeError! |
🟡 3. G – GET (Access & Find)
Reading data works exactly the same as Lists.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Index (First) | t[i] | val = t[0] | First item |
| Index (Last) | t[-i] | val = t[-1] | Last item |
| Slice | t[start:stop] | sub = t[1:3] | Sub-tuple |
| Check (Exist) | x in t | 5 in t | True / False |
| Count | .count(x) | n = t.count(5) | How many 5s? |
| Find Index | .index(x) | i = t.index(5) | Location of 5 |
| Unpack | a, b = t | x, y = (1, 2) | x=1, y=2 |
🟠 4. I – IMPROVE (Modify)
You cannot change items inside a tuple.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Update? | ❌ | t[0] = 9 | TypeError! |
| Sort? | ❌ | t.sort() | AttributeError! |
| Sort New | sorted(t) | L = sorted(t) | Returns a sorted List [...]. |
🔴 5. C – CLEAN (Deletion)
You cannot remove individual items from a tuple.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Pop? | ❌ | t.pop() | AttributeError! |
| Remove? | ❌ | t.remove(x) | AttributeError! |
| Delete All | del t | del t | Destroys variable entirely. |
🟣 6. S – STATS (Analysis)
Since tuples are read-only, math functions work perfectly on them.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Sum | sum(t) | sum((1, 2)) | 3 |
| Min | min(t) | min((1, 5)) | 1 |
| Max | max(t) | max((1, 5)) | 5 |
| Len | len(t) | len((1, 2)) | 2 |
⭐ PRO TIPS (Why use Tuples?)
Tuples are not just “worse lists.” They have special powers.
| Feature | Code Example | Why use it? |
| Variable Swap | a, b = b, a | The most Pythonic trick ever. Uses tuple packing/unpacking. |
| Dict Keys | d = {(1,2): "Home"} | Tuples can be Dictionary keys (Lists cannot!). |
| Multi-Return | return name, age | Functions can return multiple values as a single tuple. |
| Speed | (Benchmark) | Tuples are faster and use less memory than lists. |
| Safety | const data | Use tuples for data that should never change (like coordinates). |
🆚 Quick Interview Comparison
| Feature | Python List [] | Python Tuple () |
| Mutable? | ✅ Yes (Changeable) | ❌ No (Immutable) |
| Speed | 🐢 Slower | ⚡ Faster |
| Dict Keys? | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Syntax | [1, 2] | (1, 2) or just 1, 2 |
Master Python Tuples in 10 Minutes: The Ultimate M.A.G.I.C.S. Cheat Sheet
YouTube Channels:
Trendy VS Vlogs
VS Coding Academy
Join Our WhatsApp Channel for the latest job opportunities and updates:
VS_CODING_ACADEMY WhatsApp Channel
Join Our Telegram Channel for the latest job opportunities and updates: https://t.me/vscodingacademy
Open our site in Telegram Bot: https://t.me/vscodingacademy_bot
For DSA Guide: https://vscodingacademy.com/category/dsa-guide/