📖 Master Python Dictionaries with M.A.G.I.C.S.
Dictionaries (Hash Maps) are the “Heavyweight Champions” of Python data structures. They are used everywhere: from JSON APIs to databases and data science.
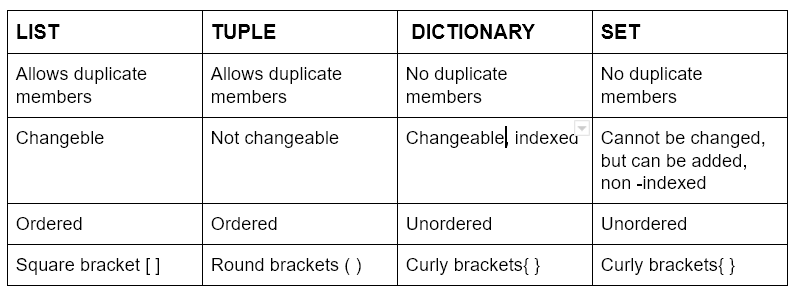
If a List is a bookshelf where you find books by number (Index), a Dictionary is a real dictionary where you find definitions (Values) by looking up a word (Key).
The Framework
| Letter | Category | Meaning | Key Methods (.) | Key Functions () |
| M | Make | Create / Copy | .fromkeys(), .copy() | {}, dict() |
| A | Add | Insert Items | d[k]=v, .update() | (None) |
| G | Get | Access / Find | .get(), .keys() | len(), in |
| I | Improve | Modify / Merge | d[k]=v, .update() | ` |
| C | Clean | Delete / Remove | .pop(), .clear() | del |
| S | Special | Loop / View | .items(), .values() | list(d) |
🟢 1. M – MAKE (Creation)
Keys must be unique and immutable (Strings, Numbers, Tuples).
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Manual Dict | {k: v} | d = {'a': 1, 'b': 2} | {'a': 1, 'b': 2} |
| Empty | {} | d = {} | {} |
| Constructor | dict() | d = dict(name="Ali", age=20) | {'name':'Ali'...} (Clean!) |
| From List | dict(list) | d = dict([('a', 1), ('b', 2)]) | Converts tuples to dict. |
| Default | .fromkeys() | d = dict.fromkeys(['a','b'], 0) | {'a': 0, 'b': 0} |
| Comprehension | {k:v for..} | d = {x: x*2 for x in range(3)} | {0:0, 1:2, 2:4} |
🔵 2. A – ADD (Growth)
Adding and Updating look exactly the same in dictionaries.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Add One | d[key] = val | d['Color'] = 'Red' | Adds new key ‘Color’. |
| Merge | .update(d2) | d.update({'Size': 'L'}) | Merges new dict into old one. |
| Set Default | .setdefault() | d.setdefault('Color', 'Blue') | Adds ‘Blue’ ONLY if ‘Color’ is missing. |
🟡 3. G – GET (Access & Find)
The #1 Rule: Never trust that a key exists. Use .get() instead of [] to prevent crashes.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Direct (Unsafe) | d[key] | v = d['name'] | Returns value. Crashes if missing. |
| Safe Access | .get(key) | v = d.get('name') | Returns None if missing (Safe). |
| Get Default | .get(k, def) | v = d.get('job', 'N/A') | Returns ‘N/A’ if ‘job’ is missing. |
| Check Key | key in d | 'age' in d | True / False |
| List Keys | .keys() | k = d.keys() | View of all keys ['a', 'b']. |
| List Values | .values() | v = d.values() | View of all values [1, 2]. |
🟠 4. I – IMPROVE (Modify)
How to update existing data.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Overwrite | d[key] = val | d['age'] = 21 | Changes ‘age’ from 20 to 21. |
| Bulk Update | .update(d2) | d.update({'age': 22}) | Updates ‘age’ from another dict. |
| Merge (New) | `d1 | d2` | `d3 = d1 |
🔴 5. C – CLEAN (Deletion)
Be careful: pop() works differently here than in lists.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Pop Key | .pop(key) | v = d.pop('age') | Removes ‘age’ and returns value (20). |
| Pop Safe | .pop(k, def) | d.pop('job', None) | Returns None if missing (Safe). |
| Pop Last | .popitem() | item = d.popitem() | Removes & returns last added pair. |
| Delete | del d[key] | del d['name'] | Deletes key ‘name’. |
| Clear | .clear() | d.clear() | Empties dict {}. |
🟣 6. S – SPECIAL (Looping Views)
Instead of “Stats”, Dictionaries have “Views” (Items).
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Items | .items() | list(d.items()) | [('name', 'Ali'), ('age', 20)] |
| Loop Keys | for k in d: | for k in d: print(k) | Loops through keys (Default). |
| Loop Both | for k,v in... | for k,v in d.items(): | Crucial: Access Key and Value in loop. |
⭐ PRO TIPS (Write Code Like an Expert)
| Feature | Code Example | Why use it? |
| Safe Get | d.get('key', 'N/A') | Avoids KeyError. Always use this for optional data. |
| Loop Unpacking | for k, v in d.items(): | The clean way to iterate. Don’t use d[k] inside a loop! |
| Sort by Key | sorted(d) | Returns a sorted list of keys. |
| Sort by Value | sorted(d.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]) | Advanced: Sorts the dictionary by its values. |
| Merge Operator | `d3 = d1 | d2` |
| Pretty Print | json.dumps(d, indent=2) | Prints nested dicts in a readable JSON format. |
🆚 Quick Interview Comparison
| Method A | Method B | Key Difference |
d['key'] | d.get('key') | [] crashes if key is missing. .get() returns None (Safe). |
del d['k'] | d.pop('k') | del just deletes. pop deletes AND gives you the value back. |
.keys() | list(d) | .keys() returns a dynamic “View”. list(d) creates a static list of keys. |
Master Python Dictionaries in 10 Minutes: The Ultimate M.A.G.I.C.S. Cheat Sheet
YouTube Channels:
Trendy VS Vlogs
VS Coding Academy
Join Our WhatsApp Channel for the latest job opportunities and updates:
VS_CODING_ACADEMY WhatsApp Channel
Join Our Telegram Channel for the latest job opportunities and updates: https://t.me/vscodingacademy
Open our site in Telegram Bot: https://t.me/vscodingacademy_bot
For DSA Guide: https://vscodingacademy.com/category/dsa-guide/
Python Dictionary Methods, Python Dict Get, Python Dictionary Operations, Python Hash Map, Python Interview Questions
