🚶 Master Python Queues with M.A.G.I.C.S.
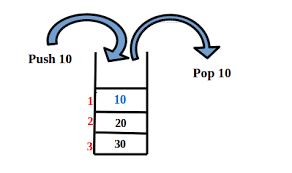
A Queue is a linear data structure that follows the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) principle.
Think of a line at a coffee shop: the first person to join the line is the first person to get served.
Crucial Warning: Never use a standard List [] for a Queue! Removing items from the front (.pop(0)) is incredibly slow. Always use collections.deque.
Python Queue Deque, Python FIFO Data Structure, Breadth First Search Python
The Framework
| Letter | Category | Meaning | Python Syntax (Using deque) |
| M | Make | Create | q = deque() |
| A | Add | Enqueue (Join Line) | .append(x) |
| G | Get | Peek (See Front) | q[0] |
| I | Improve | Restricted | (Queues preserve arrival order) |
| C | Clean | Dequeue (Leave Line) | .popleft() |
| S | Status | Check Empty | len(q) == 0 |
🟢 1. M – MAKE (Creation)
We must import deque (Double-Ended Queue) because it is optimized for fast adds and removes.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Import | from collections import deque | (Must do this first) | |
| New Queue | deque() | line = deque() | Empty Queue |
| From List | deque(list) | line = deque(["Ali", "Bob"]) | Queue with 2 people. |
| Thread Safe | Queue | from queue import Queue | (For multi-threading only) |
🔵 2. A – ADD (The “Enqueue”)
People join the back of the line.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Enqueue | .append(x) | line.append("Charlie") | Charlie joins the end. |
| Insert? | ❌ | q.insert(0, x) | Don’t do this! Use Stack or Deque rules. |
🟡 3. G – GET (The “Peek”)
Checking who is next to be served without removing them.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Peek Front | q[0] | next_person = line[0] | Returns “Ali” (First in). |
| Peek Back | q[-1] | last_person = line[-1] | Returns “Charlie” (Last in). |
| Peek Safe | if q: q[0] | if line: print(line[0]) | Prevents crash if empty. |
🟠 4. I – IMPROVE (Modify)
Queues are strict. However, deque offers a unique rotation feature.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Rotate | .rotate(n) | line.rotate(1) | Last person moves to front. |
| Reverse | .reverse() | line.reverse() | Reverses the whole line. |
🔴 5. C – CLEAN (The “Dequeue”)
Serving the customer and removing them from the front.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Dequeue | .popleft() | served = line.popleft() | Returns “Ali”. “Bob” becomes first. |
| Pop Right? | .pop() | q.pop() | Wrong! That’s a Stack operation. |
| Clear | .clear() | line.clear() | Everyone leaves the line. |
🟣 6. S – STATUS (Checks)
Always check if the line is empty before serving.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
| Is Empty? | not q | if not line: | True if empty. |
| Size | len(q) | waiting = len(line) | Count of people waiting. |
⭐ PRO TIPS (Why use Queues?)
Queues are essential for processing tasks in order.
| Feature | Code Example | Real World Use Case |
| Performance | deque vs list | popleft() is Instant (O(1)). list.pop(0) is Slow (O(n)). |
| Printer Spool | jobs.append(doc) | Printers print documents in the order they arrived (FIFO). |
| Web Server | requests.popleft() | Servers handle user requests one by one. |
| BFS Algo | (Algorithm) | Queues are the heart of Breadth-First Search (Pathfinding). |
🎥 The Visual Challenge: Hot Potato
Problem: How do you simulate a circle of kids passing a potato 2 times?
Python
from collections import deque
kids = deque(["A", "B", "C", "D"])
# Pass the potato 2 times (Rotate the circle)
kids.rotate(-2)
# 'A' and 'B' move to the back of the line.
# Now 'C' is at the front holding the potato.
print(kids[0]) # Output: 'C'Python
from queue import Queue
q = Queue(maxsize=3)
q.put(10)
q.put(20)
q.put(30)
print(q.full()) # True🧵 Python Queue (import queue) – All Methods
Python’s queue module provides thread-safe queues used in multithreading.
📦 Types of Queues
import queue
queue.Queue() # FIFO Queue
queue.LifoQueue() # LIFO Queue (Stack)
queue.PriorityQueue() # Priority Queue
🔧 Common Methods (Available in All Queue Types)
1️⃣ put(item, block=True, timeout=None)
Adds an item to the queue.
q.put(10)
2️⃣ get(block=True, timeout=None)
Removes and returns an item from the queue.
item = q.get()
3️⃣ put_nowait(item)
Adds item without blocking.
q.put_nowait(20)
Raises queue.Full if full.
4️⃣ get_nowait()
Removes item without blocking.
q.get_nowait()
Raises queue.Empty if empty.
5️⃣ empty()
Checks if the queue is empty.
q.empty()
6️⃣ full()
Checks if the queue is full.
q.full()
7️⃣ qsize()
Returns approximate queue size.
q.qsize()
8️⃣ task_done()
Signals that a previously enqueued task is complete.
q.task_done()
9️⃣ join()
Blocks until all items are processed.
q.join()
⚙️ Queue Initialization with Max Size
q = queue.Queue(maxsize=5)
maxsize = 0→ infinite queue- Used to control max elements
🚦 Exceptions in queue Module
🔹 queue.Empty
Raised when trying to get() from an empty queue.
🔹 queue.Full
Raised when trying to put() into a full queue.
📌 Example Program
import queue
q = queue.Queue(maxsize=3)
q.put(1)
q.put(2)
q.put(3)
print(q.full()) # True
print(q.get())
q.task_done()
q.join()
🧠 Summary Table
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
put() | Add item |
get() | Remove item |
put_nowait() | Non-blocking add |
get_nowait() | Non-blocking remove |
empty() | Check empty |
full() | Check full |
qsize() | Queue size |
task_done() | Task completed |
join() | Wait for tasks |
📌 Best Use Cases
- Producer–Consumer problem
- Multithreading
- Task scheduling
- Data pipelines
Master Python Queues in 10 Minutes: The Ultimate M.A.G.I.C.S. Cheat Sheet
YouTube Channels:
Trendy VS Vlogs
VS Coding Academy
Join Our WhatsApp Channel for the latest job opportunities and updates:
VS_CODING_ACADEMY WhatsApp Channel
Join Our Telegram Channel for the latest job opportunities and updates: https://t.me/vscodingacademy
Open our site in Telegram Bot: https://t.me/vscodingacademy_bot
For DSA Guide: https://vscodingacademy.com/category/dsa-guide/
Python Queue Deque, Python FIFO Data Structure, Python Deque vs List, Breadth First Search Python, Python Interview Questions
