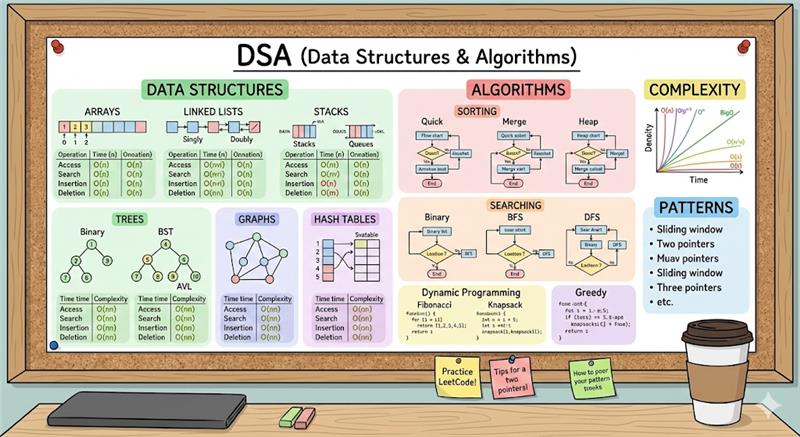
I have compiled the essence of all 11 topics into a single Grand Unified Strategy Document. This is what students should print and stick on their walls 24 hours before their interview.
“Students, stop memorizing code. Memorize the Pattern.
If you know which tool to use, the code writes itself.
Here is the decision matrix for every single data structure we have covered.”
“Students, efficiency is not just about speed; it’s about memory. A solution that uses $O(N)$ memory crashes on large datasets. A solution that uses O(1) memory scales infinitely. Here is the ultimate complexity reference for every pattern we covered.”
1. Array Patterns
The Art of Pointers & Windows.
| Problem Signal | The Algorithm Strategy | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Sorted Array + Target Sum | Two Pointers (Converge) | O(N) | O(1) |
| Contiguous Subarray + Max/Min | Sliding Window | O(N) | O(1) |
| Contiguous Sum (Negatives) | Kadane’s Algorithm | O(N) | O(1) |
| Range Queries (Sum of L…R) | Prefix Sum Array | O(1) Query | O(N) |
| Input range is 1 to N | Cyclic Sort | O(N) | O(1) |
| Sort 3 Unique Numbers | Dutch National Flag | O(N) | O(1) |
| Find Majority (> N/2) | Moore’s Voting | O(N) | O(1) |
| Rotated Sorted Array | Binary Search | O(log N) | O(1) |
2. String Patterns
Text Processing & Hashing.
| Problem Signal | The Algorithm Strategy | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Palindrome / Reverse | Two Pointers | O(N) | O(1) |
| Anagram / Permutation | Hash Map / Frequency Arr | O(N) | O(1) (26 chars) |
| Substring w/o Repeats | Sliding Window + Set | O(N) | O(26) or O(N) |
| Pattern Search | KMP Algorithm | O(N+M) | O(M) (LPS Array) |
| Prefix Search / Autocomplete | Trie (Prefix Tree) | O(L) (Length) | O(N times 26) |
| Longest Palindromic Substr | Expand Center | O(N^2) | O(1) |
| Longest Palindromic Substr | Manacher’s Algo | O(N) | O(N) |
3. Linked List Patterns
Pointer Surgery (Always aim for O(1) Space).
| Problem Signal | The Algorithm Strategy | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Cycle Detection | Floyd’s (Slow/Fast) | O(N) | O(1) |
| Find Middle Node | Slow/Fast Pointers | O(N) | O(1) |
| Intersection Point | Switch Heads | O(N+M) | O(1) |
| Reverse List | 3-Pointer Iterative | O(N) | O(1) |
| Reverse List | Recursive | O(N) | O(N) (Stack) |
| Merge Sorted Lists | Dummy Node | O(N+M) | O(1) |
| Deep Copy (Random Pointer) | Interleaving Method | O(N) | O(1) |
4. Stack & Queue Patterns
Ordering & Processing.
| Problem Signal | The Data Structure | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Nested Brackets / Undo | Stack | O(N) | O(N) |
| Next Greater Element | Monotonic Stack | O(N) | O(N) |
| Sliding Window Max | Monotonic Deque | O(N) | O(K) (Window) |
| Level-by-Level | Queue (BFS) | O(N) | O(W) (Width) |
| LRU Cache | Doubly Linked List + Map | O(1) Ops | O(Capacity) |
5. Heap & Priority Queue Patterns
Selection & Scheduling.
| Problem Goal | Which Heap? | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Find K-Largest | Min-Heap (Size K) | O(N log K) | O(K) |
| Find K-Smallest | Max-Heap (Size K) | O(N log K) | O(K) |
| Merge K Sorted Lists | Min-Heap (Values) | O(N log K) | O(K) |
| Median of Stream | Max (Left) + Min (Right) | O(log N) | O(N) |
| Task Scheduling | Max-Heap (Frequency) | O(N) | O(26) approx O(1) |
6. Greedy Patterns
Optimization Shortcuts.
| Problem Type | Strategy | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Max Activities / Meetings | Sort (End Time) | O(N log N) | O(1) |
| Fractional Knapsack | Sort (Ratio) | O(N log N) | O(1) |
| Min Platforms | Sort (Arrival/Depart) | O(N log N) | O(1) |
| Huffman Coding | Min-Heap | O(N log N) | O(N) |
7. Tree & BST Patterns
Hierarchy & Navigation.
| Problem Goal | Strategy | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Path / Height | DFS (Recursion) | O(N) | O(H) (Height) |
| Level Order View | BFS (Queue) | O(N) | O(W) (Width) |
| Sorted Data / Kth Smallest | Inorder Traversal | O(N) | O(H) |
| Common Ancestor | LCA Logic | O(N) | O(H) |
| Hard Optimization | Morris Traversal | O(N) | O(1) |
| Construct Tree | Preorder + Inorder Map | O(N) | O(N) |
8. Graph Patterns
Connections & Networks.
| Problem Goal | The Algorithm | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Shortest Path (Unweighted) | BFS | O(V+E) | O(V) |
| Shortest Path (Weighted) | Dijkstra | O(E \log V) | O(V) |
| Shortest Path (Negative) | Bellman-Ford | O(VE) | O(V) |
| Detect Cycle | DFS + Recursion Stack | O(V+E) | O(V) |
| Connectivity | Union-Find (DSU) | O(E \alpha(V)) | O(V) |
| Dependency / Scheduling | Topo Sort (Kahn’s) | O(V+E) | O(V) |
| Minimum Wire Cost (MST) | Prim’s / Kruskal’s | O(E log V) | O(V) |
9. Recursion & Backtracking Patterns
The Decision Tree.
| Problem Signal | Strategy | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Subsets / Power Set | Pick vs Don’t Pick | O(2^N) | O(N) |
| Permutations | Swap & Undo | O(N!) | O(N) |
| Maze / Word Search | Flood Fill (DFS) | O(4^{NM}) | O(NM) |
| Sudoku / N-Queens | IsSafe() + Try Next | Exponential | O(N^2) (Grid) |
10. Dynamic Programming Patterns
Recursion + Memory.
| Pattern Name | Formula | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Fibonacci / Stairs | dp[i-1] + dp[i-2] | O(N) | O(1) (Optimized) |
| Grid Paths | dp[top] + dp[left] | O(RC) | O(C) (Optimized) |
| LIS (Increasing) | max(dp[i], 1+dp[j]) | O(N^2) | O(N) |
| 0/1 Knapsack | max(Excl, Val+Incl) | O(NW) | O(W) (Optimized) |
| LCS (Strings) | 1+diag or max(up, left) | O(NM) | O(M) (Optimized) |
11. Bit Manipulation & Math Patterns
Hardware Optimization.
| Problem Goal | The Formula | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
| Odd Occurrence (Unique) | Result ^= Num | O(N) | O(1) |
| Check Power of 2 | (n & (n-1)) == 0 | O(1) | O(1) |
| Count Set Bits | n = n & (n-1) | O(Set Bits}) | O(1) |
| GCD (HCF) | gcd(b, a % b) | O(log N) | O(log N) (Stack) |
| Primes (Range) | Sieve of Eratosthenes | O(N log log N) | O(N) |
Professor’s Final Exam Tip
“Students, notice how Two Pointers and Bit Manipulation are always O(1) Space?
If the interviewer says ‘Optimize for Space’, run to those two patterns immediately.
“If you are blank in an interview:
- Can I sort it? (Two Pointers)
- Can I use a Map? (Hashing)
- Is it a tree/graph? (BFS/DFS)
- Is it optimization? (DP/Greedy)
“Students, notice how Two Pointers and Bit Manipulation are always O(1) Space? If the interviewer says ‘Optimize for Space’, run to those two patterns immediately.
Start Brute Force, then apply the pattern. Good luck.”
Good luck. You are now ready.”
12)The DSA Cheat Sheet: 11 Essential Pattern Tables (Time & Space Complexity Included)
DSA Cheat Sheet, Coding Interview Patterns, Time and Space Complexity Chart, Algorithm Revision Sheet
YouTube Channels:
Trendy VS Vlogs
VS Coding Academy
Join Our WhatsApp Channel for the latest job opportunities and updates:
VS_CODING_ACADEMY WhatsApp Channel
Join Our Telegram Channel for the latest job opportunities and updates: https://t.me/vscodingacademy
Open our site in Telegram Bot: https://t.me/vscodingacademy_bot
For DSA Guide: https://vscodingacademy.com/category/dsa-guide/
